Speeches Shim
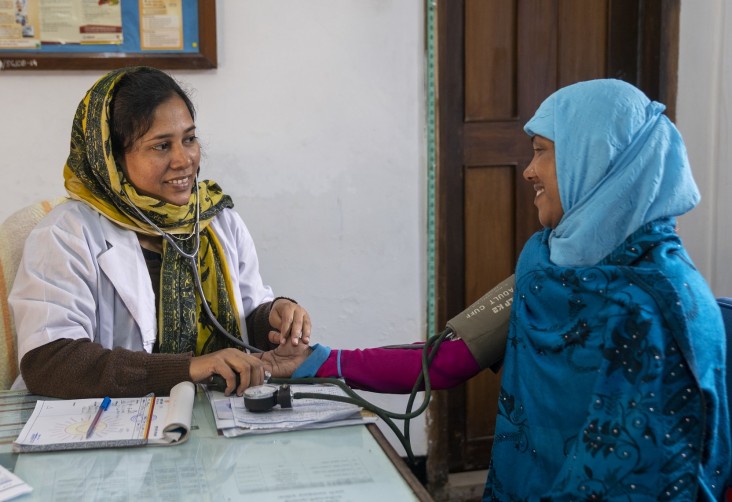

Bangladesh has made impressive progress in many of the health-related indicators over the past few decades. However, challenges still remain. Although Bangladesh is one of the few countries to achieve its Millennium Development Goal in reducing childhood mortality well ahead of 2015, the decline in under-five mortality has stalled in recent years. Maternal mortality ratio also fell sharply between 2001 and 2010, but has stagnated at 196 maternal deaths per 1,000 live births since then. Now half of the child births take place in health facilities compared to 17 percent just a decade ago, but health facilities are not fully prepared to provide quality health services. In response, USAID focuses on improving maternal and child health, expanding family planning and reproductive health, integrating family planning and nutrition into basic health care, and strengthening public health systems to improve the quality and availability of services across the country. USAID also supports the Government of Bangladesh (GOB) in its efforts to reduce the burden of tuberculosis (TB), and contributes to the Bangladesh government’s Health, Population, and Nutrition Sector Program.
Improving Maternal and Child Health
To continue gains made in maternal and child health, USAID trains community health workers and clinic staff to help them provide high-quality care during childbirth. USAID also teaches health workers to use a simple resuscitation device to prevent asphyxia during birth and apply antiseptic to babies’ umbilical cords to prevent infection. USAID outreach and mobile health initiatives encourage pregnant women and their families to ensure they attend antenatal checkups and give birth under the supervision of a skilled health worker.
Expanding Use of Family Planning
While more than half of all Bangladeshi couples use modern methods of contraception, the Bangladesh government aims to increase contraceptive use to 72 percent. To this end, USAID works with local partners to ensure that men, women, and couples have access to high-quality reproductive health services. USAID and the GOB have developed a public awareness strategy to promote the benefits of family planning, proper birth spacing, and contraceptives. USAID also conducts research to evaluate family planning programs and utilize innovative technology to maximize reach and efficiency in providing reproductive health services.
Integrated Health Care Services
Sixty-two percent of all Bangladeshi couples use contraception, and the Bangladesh government aims to increase contraceptive use to 75 percent. To this end, USAID works with local partners to ensure that men, women, and couples have access to high-quality reproductive health services. USAID and the GOB have developed a public awareness strategy to promote the benefits of family planning, birth spacing, and contraceptives. USAID also conducts research to evaluate family planning programs and make use of innovative technology to maximize reach and efficiency in providing reproductive health services.
Strengthening Health Systems and Governance
USAID assists Bangladesh to strengthen its public health systems with an emphasis on improving primary health care delivery at the community level. At the national level, USAID programs work with public health leaders to improve policy and planning, financial management, monitoring and evaluation, procurement, and logistics. We also support the government’s national TB program, providing financial support and technical assistance to upgrade TB laboratory technology and procure drugs to treat multidrug resistant TB patients.
Results
In 2019, USAID programs in Bangladesh:
- Provided over 46 million health service consultations through an extensive network of 399 NGO clinics, 10,000 satellite clinics, and 7,300 community health volunteers. Provided over 35 million health service consultations through an extensive network of 369 NGO clinics, 10,000 satellite clinics, and 7,300 community health volunteers.
- Provided family planning and reproductive health services through over 209,000 public, private and NGO sector service/commodity outlets. USAID programs currently account for over one-third of Bangladesh's modern contraceptive use.
- Strengthened GOB’s health systems that enabled 122 public sector clinics in under-served areas to provide 24/7 (at any time of any day) delivery services.
- Advanced technological solutions to detect deadly multi-drug resistant TB within two hours; digitize the national health information system to improve services; and establish an electronic logistics management information system to streamline the government’s procurement and distribution of 25 life-saving drugs and family planning commodities.

Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.