Speeches Shim
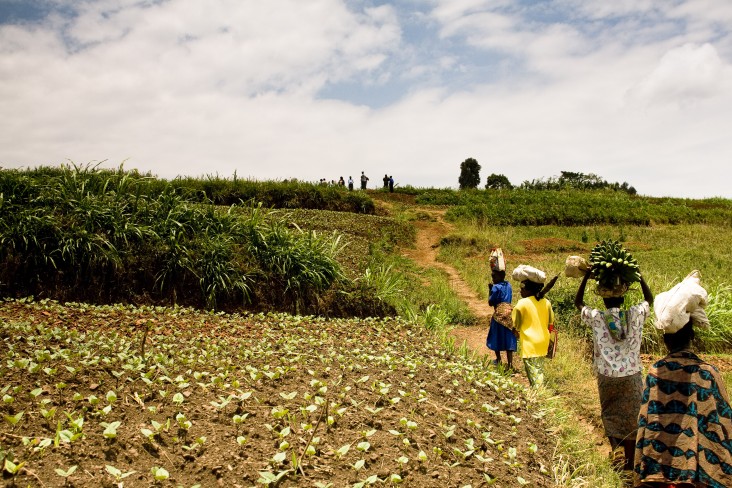

Agriculture employs 70 percent of the labor force, and the country's solid growth record and macroeconomic stability provide a solid foundation for agricultural investment. The country has committed to generating sustained agricultural growth, increasing the share of the national budget allocated to agriculture from 3 percent in 2006 to 10.01 percent in 2015. these investments appear to be paying off, with annual agriculture growth averaging over 6 percent since 2007.
Despite the gains, agricultural productivity remains low and the levels of chronic malnutrition remain unacceptably high at 38 percent for children under 5 years old. Through Feed the Future, USAID is promoting inclusive agricultural growth throughout the country.
Current agricultural programs build on years of progress and accomplishment. Our support increases productivity in targeted value chains such as maize, beans and dairy and other high value crops. The programs also help farmers increase access to and adoption of nutrition-sensitive agricultural technologies to improve their capacity to manage natural resources and to adapt to climate shocks.
Encouraging private sector growth and competitiveness in the agriculture sector is a priority. In the staple crop, dairy and horticulture sectors, our work has increased the productivity and profitability of business actors and improved the lives of rural Rwandans, providing training and equipment that helps increase the quantity, quality, and market demand of agricultural products. We also support private sector engagement through a project to assist the Ministry of Agriculture to attract private investments, strengthen agricultural value chains, provide services to businesses, and build capacity for greater investment in agriculture. To facilitate agricultural crops production’s access to market, we've also worked with the World Bank to rehabilitate at least 500 km of rural feeder roads.

Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.